File Batch Renamer
Python 批量重命名文件
- 一个基于Python的终极重命名机
- a file batch renamer based on python (include Chinese)
- 用于自动对文件夹里大部分类型的文件进行分析,并批量重命名
- 重命名文件自古就是繁琐事情,谁用谁指导
- 方便处理IT办公文件和下载文件夹的杂乱文件
- 简单练手,练手第三方包,编写环节综合到各方面,python初学者必备
- 基于云端和本地,也可以本地
- 对小白提供(exe),云端提供临时服务器
Tika版架构
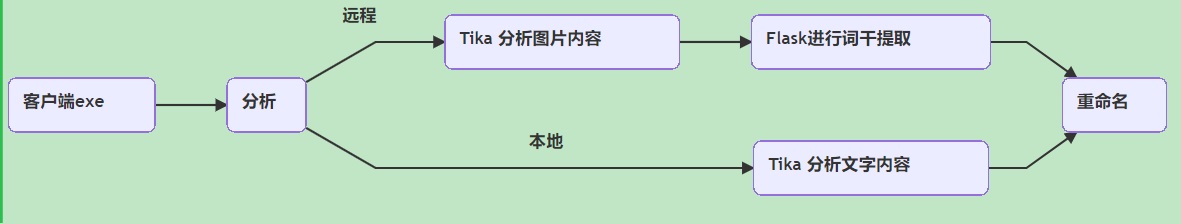
(假如条件不允许可以全部本地化)
Updated
- Updated 2019.8.10:
- Apache Tika 版改进,基于云端和本地,终极自动重命名机
- Updated 2019.1.2:
- 新版 Apache Tika 解析全文件版本
- 旧版 Python 3rd party 解析文件版本
Docx Content Modify

邮单自动批量生成器
- 法院法务自动化批量生成邮寄单据-Legal agency postal notes automatically generate app
- 给予法务邮递人员从法务OA数据表(excel)和公开的判决书(docx)提取当事人地址内容,批量直接生成邮单。 减轻相关员负担,尤其系列案,人员多地址多,手工输入地址重复性劳动太多,信息容易错漏
环境
- conda : 4.6.14
- python : 3.7.3.final.0
- Win10 + Spyder3.3.4 (打开脚本自上而下运行,或者自己添加main来py运行)
- 组件: python-docx,pandas,StyleFrame,configparser
- 打包程序: pyinstaller
更新
【2019-6-19】
- 添加合并系列案功能,节省打印资源
【2019-6-12】
- 更新判决书过滤词汇
内容
- [x] 按格式重命名判决书
- [x] 提取判决书人员和地址信息
- [x] 自动重命名为 判决书_AAA号_原_BBB号.docx
- [x] 拷贝OA表记录到Data表
- [x] 按数量提取,按日期提取,按指定案号提取
- [x] 整理Data表格式,对表中数据的变形,清洗,符合打印邮单的字段格式
- [x] 填充判决书信息到Data表
- [x] 按照Data表输出寄送邮单
- [x] 填充好所有信息,再次运行就能输出Data表指定邮单
Car Evaluation Analysis
汽车数据R语言机器学习分析
- title: “Car Evaluation Analysis”
- author: “Suraj Vidyadaran”
- date: “Sunday, February 21, 2016”
- output: md_document
对汽车数据使用17种分类算法进行数据分析,对代码进行实践应用和内容翻译
Data Scientists Toolbox Course Notes
数据科学工具课程笔记
数据科学工具课程,包含命令行,R语言,Markdown等用法
CLI (命令行 Command Line Interface)
/= root directory~= home directorypwd= print working directory (current directory)clear= clear screenls= list stuff-a= see all (hidden)-l= details
cd= change directorymkdir= make directorytouch= creates an empty filecp= copycp <file> <directory>= copy a file to a directorycp -r <directory> <newDirectory>= copy all documents from directory to new Directory *-r= recursive
rm= remove-r= remove entire directories (no undo)
mv= movemove <file> <directory>= move file to directorymove <fileName> <newName>= rename file
echo= print arguments you give/variablesdate= print current date
GitHub 代码仓库
- Workflow
- make edits in workspace
- update index/add files
- commit to local repo
- push to remote repository
git add .= add all new files to be trackedgit add -u= updates tracking for files that are renamed or deletedgit add -A= both of the above- Note:
addis performed before committing
- Note:
git commit -m "message"= commit the changes you want to be saved to the local copygit checkout -b branchname= create new branchgit branch= tells you what branch you are ongit checkout master= move back to the master branchgit pull= merge you changes into other branch/repo (pull request, sent to owner of the repo)git push= commit local changes to remote (GitHub)
JHU Coursera Rprogramming Course Project 3
医院病例数据分析项目
JHU DataScience Specialization/Cousers Rprogramming/Week3/Course Project 3
作业练习目标:通过分析医院数据,编写函数,通过函数分析各州医院指定的病例排名
- [x] 数据源:outcome-of-care-measures.csv
Contains information about THIRTY(30)-day mortality and readmission rates for heart attacks,heart failure, and pneumonia for over FOUR THOUSAND (4,000) hospitals;
- [x] 说明书:Hospital_Revised_Flatfiles.pdf
30天死亡最率最低的医院
输出指定州(例子德州TX)函数(best)
1 | best <- function(state, outcome) { |
例子:输出指定州(德州TX)30天死亡最率最低的医院
1 | ## Warning in which.min(df[, 2]): 强制改变过程中产生了NA |
1 | ## [1] "Hospital with lowest 30-day death rate is: CYPRESS FAIRBANKS MEDICAL CENTER" |
心脏病死亡率最低医院
输出前10字母排名州的心脏病死亡最低医院(rankall)
JHU Coursera Rprogramming Assignment 2
Programming Assignment 2 函数与缓存作业
JHU DataScience Specialization/Cousers R Programming/Week2/Programming Assignment 2
This two functions below are used to create a special object that stores a numeric matrix and cache’s its inverse
第一步编写一个函数存储四个函数
makeCacheMatrix creates a list containing a function to 1. set the value of the matrix 2. get the value of the matrix 3. set the value of inverse of the matrix 4. get the value of inverse of the matrix
1 | makeCacheMatrix <- function(x = matrix()) { |
JHU Coursera Datatools Course Project
Datatools Course Project 数据工具项目
JHU DataScience Specialization/Cousers The Data Scientist’s Toolbox/Week??/Course Project
由于这个非常入门的课程,共4Week每周一个小quiz,这个应该是最后的Project忘记了
主要是熟练掌握一些R语言的数据处理工具例如 xlsx,XML等格式,以及readr这些有用的R包用法
以下代码下载资源比较大暂不执行有兴趣的读者可以自己尝试
读取csv格式 2006年美国社区调查(ACS)
The American Community Survey distributes downloadable data about United States communities. Download the 2006 microdata survey about housing for the state of Idaho using download.file() from here:
- (pid, Population CSV file)
- (hid, Household CSV file)
说明书 PUMS 说明书 DATA DICTIONARY - 2006 HOUSING PDF
1 | fileUrl <- "https://d396qusza40orc.cloudfront.net/getdata%2Fdata%2Fss06pid.csv" |
读取几十上百m的数据算大文件,运算应该考虑花销
1 | ## Unit: milliseconds |
1 | ## Unit: milliseconds |
1 | ## Unit: microseconds |
1 | pander(arrange(A,mean)) |
| expr | min | lq | mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| PID <- fread(file = “Fss06pid.csv”, fill = T) | 13.4 | 13.4 | 13.4 |
| read.csv(file = “Fss06pid.csv”) | 422.6 | 422.6 | 422.6 |
| read_csv(file = “Fss06pid.csv”) | 627 | 627 | 627 |
| median | uq | max | neval |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13.4 | 13.4 | 13.4 | 1 |
| 422.6 | 422.6 | 422.6 | 1 |
| 627 | 627 | 627 | 1 |
1 | pander(arrange(B,mean)) |
JHU Coursera Regression Model Quizes
JHU Coursera Regression Model Quizes 回归模型问题集
JHU DataScience Specialization/Cousers Reproducible Data/Week1-4/Regression Model Quizes
主要练习手工计算回归模型的基础方法
Week 2
Quiz 1
手算均值
1 | x <- c(0.18, -1.54, 0.42, 0.95) |
1 | ## [1] "mean of y is : 0.147143" |
Quiz 2
线性回归
1 | x <- c(0.8, 0.47, 0.51, 0.73, 0.36, 0.58, 0.57, 0.85, 0.44, 0.42) |
| Estimate | Std. Error | t value | Pr(> | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 1.567 | 1.252 | 1.252 | 0.246 |
| x | -1.713 | 2.105 | -0.8136 | 0.4394 |
1 | pander(lm(y~x-1)) #去除截距 |
| Estimate | Std. Error | t value | Pr(> | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | 0.8263 | 0.5817 | 1.421 | 0.1892 |
Quiz 3
mtcars 回归系数
| (Intercept) | wt |
|---|---|
| 37.29 | -5.344 |
Quiz 4
练习求b1
\[\begin{align} Cor(Y,X) &= 0.5 \qquad Sd(Y) = 1 \qquad Sd(X) = 0.5 \\ \beta_1 &= Cor(Y,X) * \frac{Sd(Y)}{Sd(X)} \end{align}\]
1 | B1 = 0.5 * 1 / 0.5 |
Quiz 5
1 | corr <- .4; emean <- 0; varr1 <- 1 |
1 | ## [1] 0.6 |
Quiz 6
1 | x <- c(8.58, 10.46, 9.01, 9.64, 8.86) |
1 | ## [1] -0.9718658 1.5310215 -0.3993969 0.4393366 -0.5990954 |
Quiz 7
1 | x <- c(0.8, 0.47, 0.51, 0.73, 0.36, 0.58, 0.57, 0.85, 0.44, 0.42) |
| Estimate | Std. Error | t value | Pr(> | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 1.567 | 1.252 | 1.252 | 0.246 |
| x | -1.713 | 2.105 | -0.8136 | 0.4394 |
Quiz 8
It must be identically 0.
Quiz 9
1 | x <- c(0.8, 0.47, 0.51, 0.73, 0.36, 0.58, 0.57, 0.85, 0.44, 0.42) |
1 | ## [1] 0.573 |
Quiz 10
\[\begin{align} \beta_1 &= Cor(Y,X)*Sd(Y)/Sd(X) \\ Y_1 &= Cor(Y,X)*Sd(X)/Sd(Y) \\ \beta_1/Y_1 &= Sd(Y)^2/Sd(X)^2 \notag \\ &= Var(Y)/Var(X) \end{align}\]




